Network Failover Configuration
1. What is Network Failover?
Network Failover refers to a process by which the system automatically switches to a standby network connection in the event of a failure of the primary network connection. This ensures that network services remain available without interruption, maintaining business continuity and minimizing downtime.
2. Login:
Login using DNS server IP address ( For Ex = 192.168.10.1)
3. Dual SIM Network Failover:
3.1 Condition 1 :
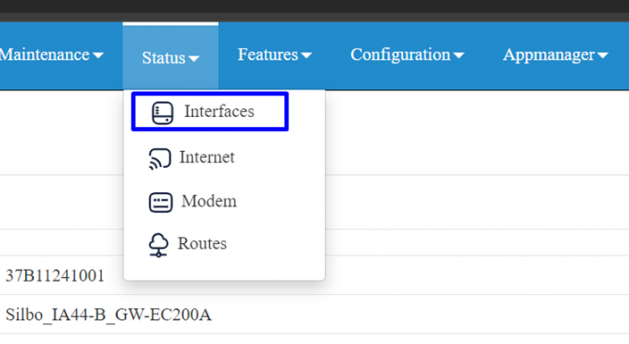
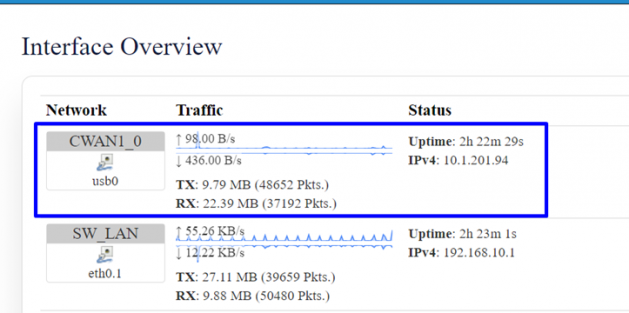
Go to status=> interfaces, by default CWAN1_0 ( i.e SIM 1) status should be UP, based on the priority that has been set ( can be changeable).
Other way to check which SIM is currently active is click on
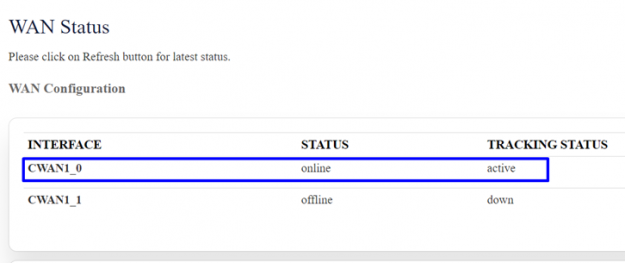
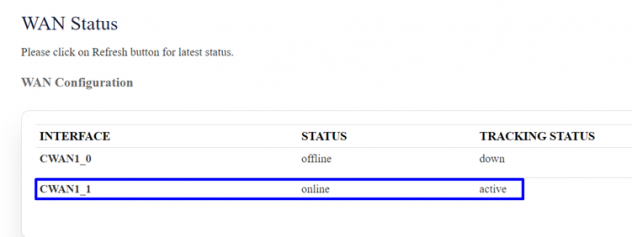
Status=> internet , In WAN status CWAN1_0 (i.e SIM 1) should be online/active.
3.2 Condition 2:
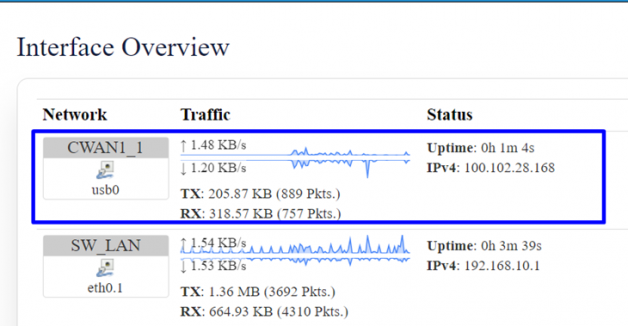
In case of SIM 1 failure , CWAN1_1 (i.e SIM 2) should get latched to the network.
Go to status=> interfaces , CWAN1_1 (i.e SIM2) should be UP.
Go to status=>internet, CWAN1_1 (SIM 2) should be online/active.
3.3 Condition 3:
If both SIM faces network failure, Wi-Fi WAN will act as backup.
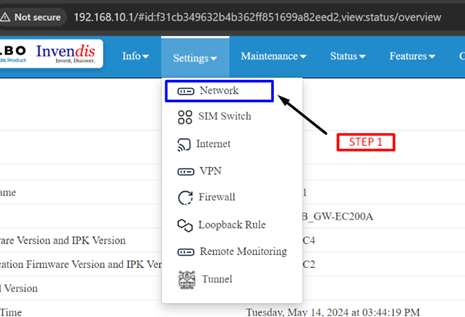
- Step 1: Click on settings=>network=>wifi settings
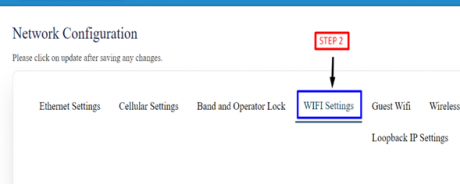
- Step 2: In general settings click on radio mode and from dropdown select Access point and Client.
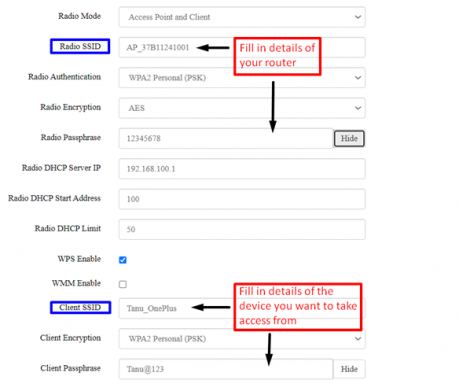
- Step 4: Go to status=> interfaces, Wi-Fi WAN should be UP.
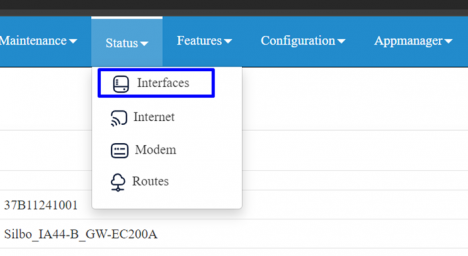
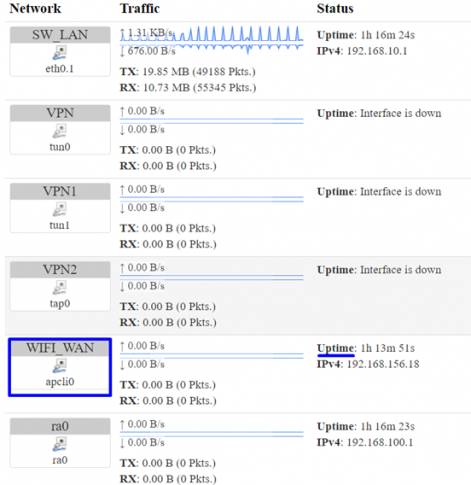
4. Conclusion:
- In conclusion, these are one of the many configurations to make for ensuring continuous network availability and minimizing downtime in the event of network failures.