IAB44C User Manual
'
Connecting with the device to the System (Laptop/Desktop)
To log in to SILBO_IAB44-C by connecting the router to your laptop or desktop via LAN or using Wi-Fi, please follow the steps below.
Connecting via LAN:
Connect your laptop's LAN port to one of the router's LAN interfaces. Ensure that you select any LAN interface (there is one available) while making sure the WAN interface is not used.
How to connect with the SILBO_IAB44-C application
Once the LAN connection is established between the device and the laptop or the desktop
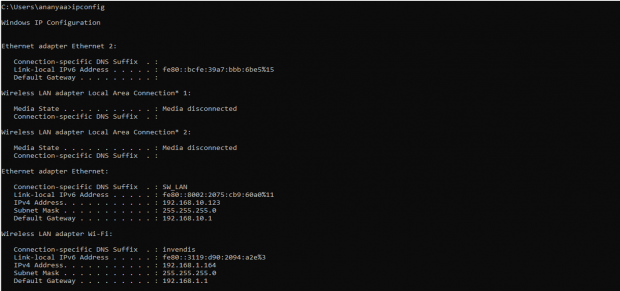
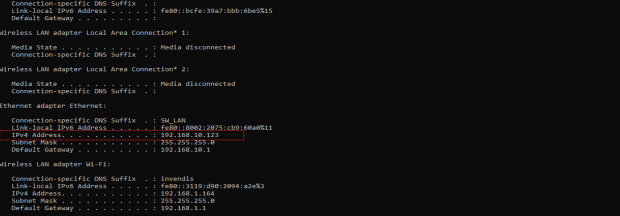
Please open the command prompt and ping to get the IP config of that device.
Type the command Ipconfig
It will provide the Ip address/url of that device through which the application can be accessed.
Log In
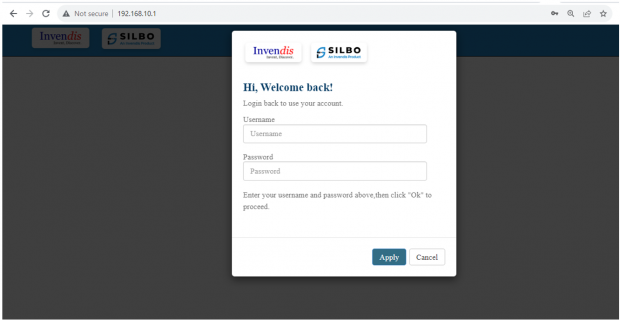
Open the web browser and type the IP address in the URL.
It will show the log in page of the application.
Give the valid credentials for the username and password to login to the application page.
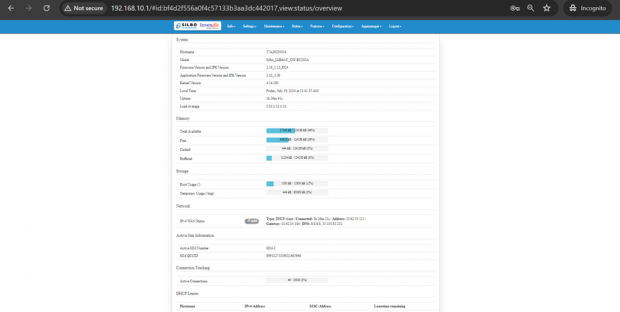
Once the user credentials are provided it will direct to the landing page of the application.
The “Status” landing page shows all the detailed specification of the device like system, memory storage and connection tracking etc.
The application is divided in to 8 Modules.
- Info
- Settings
- Maintenance
- Status
- Features
- Configuration
- Appmanager
- Logout
1. Info
The “Info” module provides the information about the devices to the user.
It provides all the specification related to the hardware, firmware, Networks and the Connection uptimes.
It has 3 submodules.
- Overview
- System Log
- Kernel Log
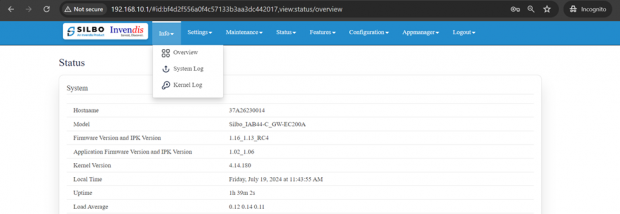
1.1 Overview
In overview module it displays all the specification categorically of a device like System, Memory, storage, Connection tracking, DHCP Lease.
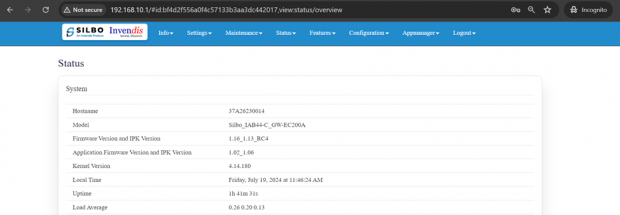
System:
In this section it displays the hardware configured specification of the device.
The specifications details are as follows,
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Hostname | 37A26230014 | This field displays the router serial number of the device |
| 2 | Model | Silbo_IAB44-C_GW-EC200A | This field displays the model number of the device |
| 3 | Firmware Version and IPK Version | 1.16_1.13_RC3 | This field displays the firmware version and IPK version |
| 4 | Application Firmware version and IPK version | 1.02_1.06 | This field displays the software version of the device. |
| 5 | Kernel Version | 4.14.180 | This field displays the kernel version of the device |
| 6 | Local Time | Friday, July 19, 2024 at 11:52:23 AM | This field displays the local time |
| 7 | Uptime | 1h 48m 3s | This field displays the uptime of the device |
| 8 | Load Average | 0.66 0.29 0.17 | This field displays the average load |
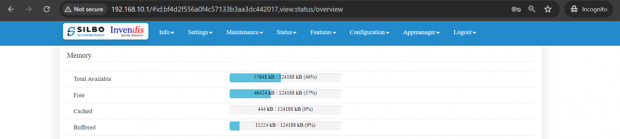
Memory:
In this section it displays the memory configured specification of the device.
The specifications details are as follows.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Total Available | 57716 kB / 124188 kB (46%) | This field displays the total availability of memory space in the device |
| 2 | Free | 46424 kB / 124188 kB (37%) | This field displays the Free memory space in the device |
| 3 | Cached | 444 kB / 124188 kB (0%) | This field displays the Cached memory space in the device |
| 4 | Buffered | 11224 kB / 124188 kB (9%) | This field displays the Buffered memory space in the device |
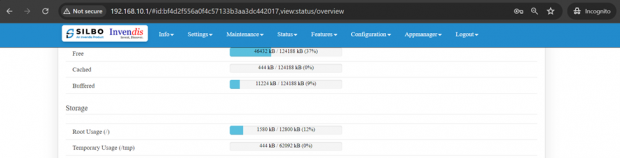
Storage:
In this section it displays the status of storage as root and temporary usage specification of the device.
The specifications details are as follows.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Root Usage | 1580 kB / 12800 kB (12%) | This field displays the total root usage of the device |
| 2 | Temporary Usage | 444 kB / 62092 kB (0%) | This field displays the total temporary usage of the device |
Network:
In this section you can monitor IPv4 WAN status.
The specifications details are as follows.
| SN | Field Name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Type | DHCP client | A DHCP client is a device or software that requests and receives configuration information from a DHCP server, such as an IP address, gateway, and DNS servers. |
| 2 | Connected | 1h 49m 8s | This indicates the duration for which the device has been connected to the network. |
| 3 | Address | 10.62.35.111 | This is the IP address assigned to the DHCP client by the DHCP server. It uniquely identifies the device on the network. |
| 4 | Gateway | 10.62.35.144 | The gateway (or default gateway) is the IP address of the network device that routes traffic from the local network to other networks. |
| 5 | DNS | 8.8.8.8, 10.103.81.232 | The first DNS server "8.8.8.8" is a public DNS server provided by Google.
The second DNS server "10.103.81.232" is a private DNS server. |
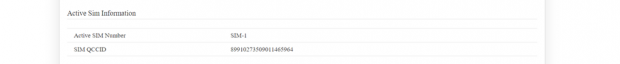
Active SIM Information:
This section displays SIM details only when the SIM card is active.
Connection Tracking:
In this section it displays the status of connection tracking for the device.
The specifications details are as follows.
| SN | Field Value | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Active Connections | 48/16384 (0%) | This field displays the active connection of the device. |
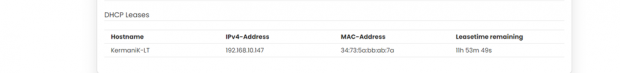
DHCP Leases:
In this section it displays the DHCP lease of the temporary assignment of an IP address to a device on the network.
The specifications details are below.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Host Name | KermaniK-LT | This field displays the configured Host Name/Username for that device. |
| 2 | IPv4-Address | 192.168.10.147 | This field displays the IP address of the device. |
| 3 | MAC-Address | 34:73:5a:bb: ab:7a | This field displays the MAC-Address of the device. |
| 4 | Lease time remaining | 11h 53m 49s | This field displays the lease time remaining for the device. |
1.2 System Log
This page provides on screen System logging information. In this page the user gets to view the system logs.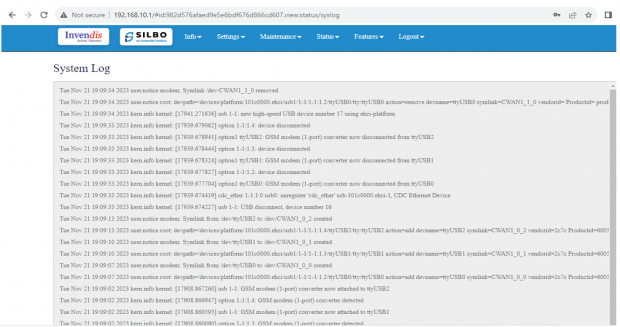
1.3 Kernel Log
This page provides on screen Kernel logging information.
In this page the user gets to view the Kernel logs.
2. Setting
In this “Setting” module the user can Configure/update all the required parameters related to Network, SIM Switch, Internet, VPN, Firewall, Loopback Rule, Remote monitoring, Tunnel as per requirement.
IT consist of 8 submodules.
- Network
- Sim Switch
- Internet
- VPN
- Firewall
- Loopback Rule
- Remote Monitoring
- Tunnel
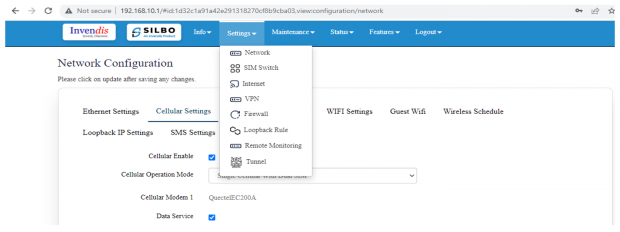
2.1 Network
In this section the user does all the setting related configuration with reference to network like Ethernet Setting, Cellular Setting, Band lock and Operator Lock, Wi-Fi, Guest Wi-Fi, Wireless Schedule, SMS Setting, Loopback IP.
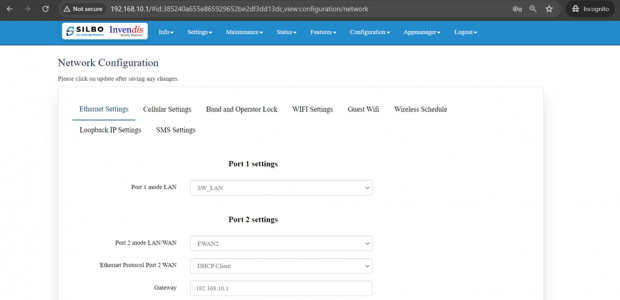
Ethernet Setting:
In this page it will display all the configured port that is attached with the device.
For this device 2 ports are configured. Ethernet mode can be configured as WAN and as LAN as well. Ethernet LAN Connection settings can be configured as DHCP server or Static.
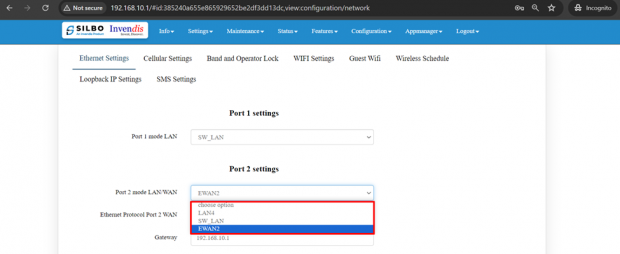
For port 2 settings,
Port 2 is convertible from WAN to LAN while EWAN2(WAN) stays by default.
Note: After any changes made, save and update the page below.
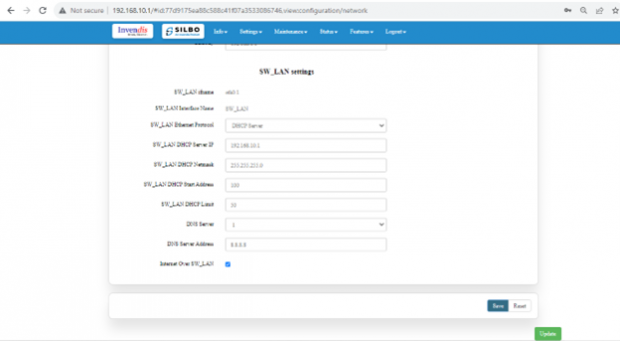
SW_LAN settings,
In this part the user can configure the setting for SW_LAN.
Note: After any changes made, save and update the page below.
The specifications details are below.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | SW_LAN Ethernet Protocol | DHCP Server | This field displays the Ethernet mode selection. |
| 2 | SW_LAN DHCP Server IP | 192.168.10.1 | This field displays DHCP server IP configured which can be changed accordingly. |
| 3 | SW_LAN DHCP Netmask | 255.255.255.0 | This field displays DHCP server Netmask address configured. |
| 4 | SW_LAN DHCP Start Address | 100 | This field displays DHCP server start address configured. |
| 5 | SW_LAN DHCP Limit | 50 | This field displays DHCP server limit. |
| 6 | DNS Server | 1 | This filed display number of DNS server availability. |
| 7 | DNS Server Address | 8.8.8.8 | This filed display the DNS server address. |
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
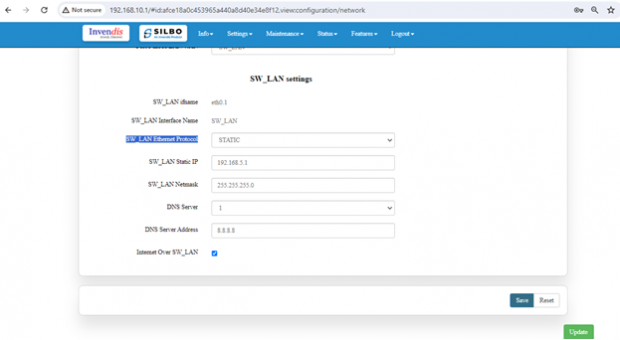
Static option for SW_LAN Ethernet Protocol:
Select the option of static from the drop-down menu for SW_LAN Ethernet Protocol.
Note: After any changes made, save and update the page below.
The specifications details are below.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | SW_LAN Ethernet Protocol | Static | This field displays the Ethernet mode selection |
| 2 | SW_LAN static IP | 192.168.5.1 | This field displays static server IP configured. |
| 3 | SW_LAN Netmask | 255.255.255.0 | This field displays static server Netmask address configured |
| 4 | DNS Server | 1 | This filed display number of DSN server availability |
| 5 | DSN Server Address | 8.8.8.8 | This filed display the DSN server address. |
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
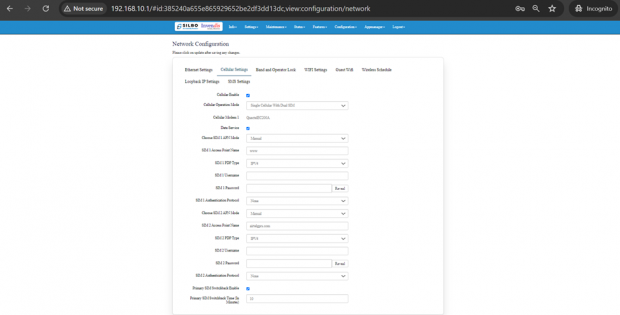
Cellular Setting:
In this page, the user needs to configure the various details with respect to the SIM.
Select single cellular single sim where the user must configure the APN details of the sim used for the router device. The Configurations can be done based on the SIM usage, with respect to IPV4 or IPV6.
The specifications details are below.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Cellular Enable | Checkbox | Check this box to enable cellular functionality. |
| 2 | Cellular Operation Mode | 1.) Single Cellular with Dual Sim
2.) Single Cellular with Single SIM |
1.) This mode allows you to use one cellular modem with two SIM cards.
2.) This mode allows you to use one cellular modem with single SIM card. |
| 3 | Cellular Modem 1 | QuectelEC200A | This field displays the modem name. |
| 4 | Choose SIM 1 APN Mode | 1.) Auto
2.) Manual |
1.) Choose Auto for regular SIM to detect APN name automatically.
2.) Choose manual to enter the APN settings manually in case of M2M SIM cards. |
| 5 | SIM 1 Access Point Name | airtelgprs.com | Enter the APN provided by your cellular service provider in case of M2M sim. For regular sim cards APN name will be displayed automatically. |
| 6 | SIM 1 PDP Type | IPV4 | Choose the PDP type, which is typically either IPv4 or IPv6 depending on the sim card. |
| 7 | SIM 1 Username | Enter the username if required by the APN. Leave blank if not required. | |
| 8 | SIM 1 Password | Enter the password if required by the APN. Leave blank if not required. | |
| 9 | SIM 1 Authentication Protocol | None | Choose the authentication protocol. Options typically include None, PAP, or CHAP. |
| 10 | Choose SIM 2 APN Mode | 1.) Auto
2.) Manual |
1.) Choose Auto for regular SIM to detect APN name automatically.
2.) Choose manual to enter the APN settings manually in case of M2M SIM cards. |
| 11 | SIM 2 Access Point Name | airtelgprs.com | Enter the APN provided by your cellular service provider in case of M2M sim. For regular sim cards APN name will be displayed automatically. |
| 12 | SIM 2 PDP Type | IPV4 | Choose the PDP type, which is typically either IPv4 or IPv6 depending on the sim card. |
| 13 | SIM 2 Username | Enter the username if required by the APN. Leave blank if not required. | |
| 14 | SIM 2 Password | Enter the password if required by the APN. Leave blank if not required. | |
| 15 | SIM 2 Authentication Protocol | None | Choose the authentication protocol. Options typically include None, PAP, or CHAP. |
| 16 | Primary SIM Switchback Time (In Minutes) | 10 | Enter the time in minutes after which the system should switch back to the primary SIM if it becomes available. |
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
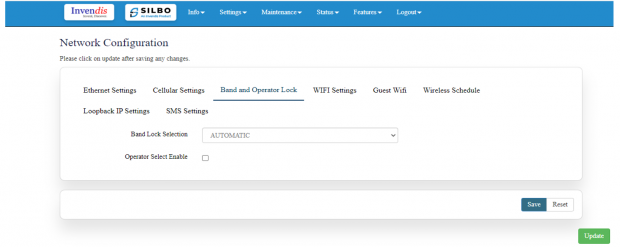
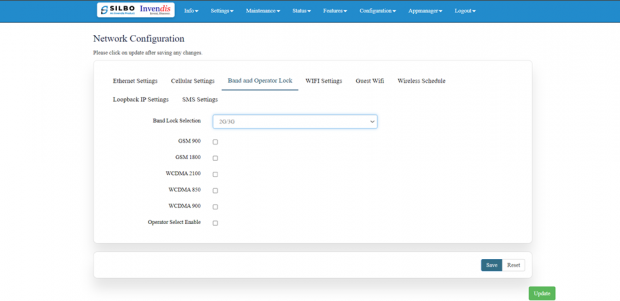
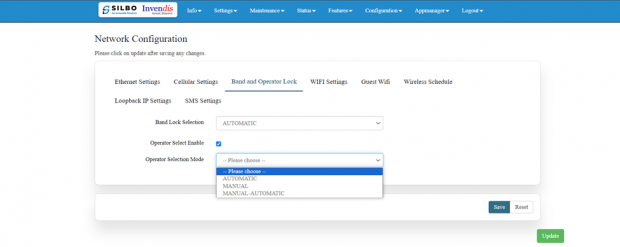
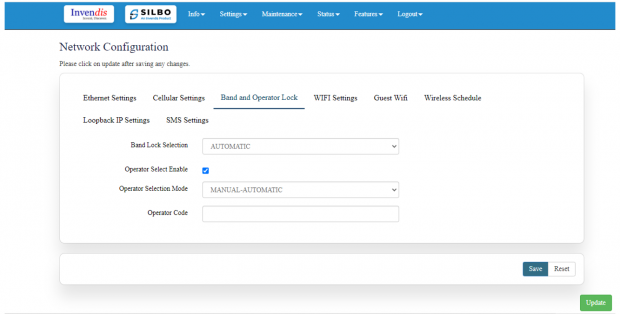
Band lock and Operator Lock:
In this page, the user needs to configure the lock band and operator based on the service provider.
Bands available in the drop-down list.
2G/3G option:
2G/3G: - 3G allows additional features such as mobile internet access, video calls and mobile TV. While the main function of 2G technology is the transmission of information through voice calls.
The user should select the band check box available for 2g/3g from the given list. Bands available for selection under LTE for the bands available in that area.
Operator Selection Mode:
The user needs to click on the check box of the “operator select enable” to select the operator.
Once the check box is clicked there will be a dropdown list of the operator modes from which the user needs to select the mode. The user needs to select the operator mode from the given dropdown list.
If the user selects the mode “Manual” or “Manual-Automatic” then one more text box will appear where the user must provide the operator code.
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
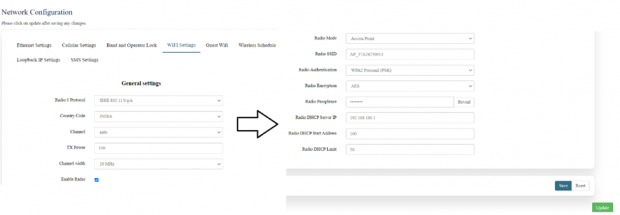
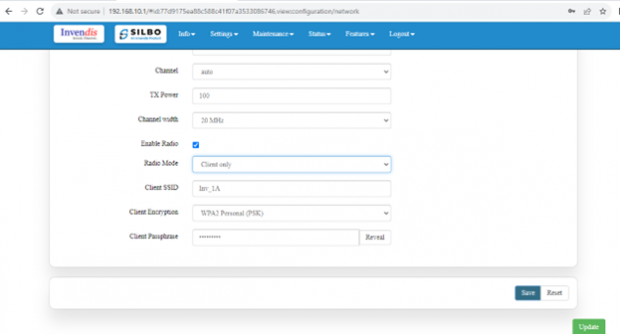
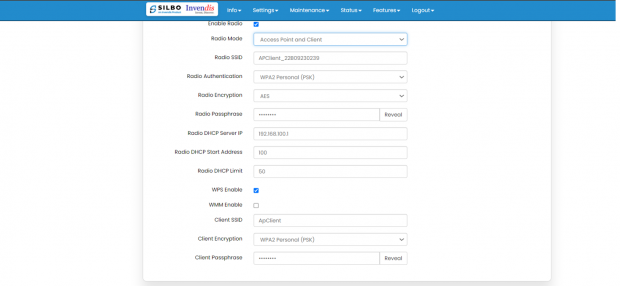
Wi-Fi Setting:
In this, router has the general setting and change country code, channel, radio mode, radio passphrase as per the requirement after clicking on enable Radio button.
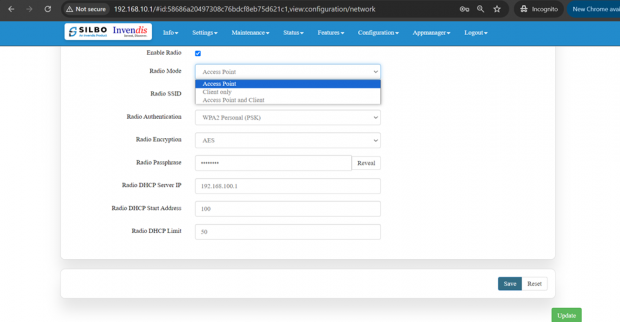
The user needs to select the respective radio mode based on its need.
It has 3 radio modes.
‘Access point’, ‘client only’ and ‘Access point and client’
Refer the below picture.
Access Point mode:
In Access Point mode, a configuration in which a router, allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network by creating a Wi-Fi hotspot.
Client point:
In client mode, the access point connects your wired devices to a wireless network. This mode is suitable when you have a wired device with an Ethernet port and no wireless capability, for example, a smart TV, Media Player, or Game console and you want to connect it to the internet wirelessly, select the Client Mode and give the Radio SSID & client passphrase.
Access point and client point:
Select this option for both type of connection, give both SSID and passphrase.
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
The specifications details are below.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Radio 0 Protocol | IEEE 802.11 b/g/n | This section shows the radio protocol which is by default. |
| 2 | Country Code | INDIA | Select the country accordingly.
(INDIA by default) |
| 3 | Channel | Auto | In this dropdown the user should select the proper channel to be used. (Auto by default) |
| 4 | TX Power | 100 | In this text box the user should specify the power. |
| 5 | Channel Width | 20 MHz | In this dropdown the user should select the channel width |
| 6 | Radio Mode | 1.) Access point
2.) Client only 3.) Access point and client |
In this drop down the user should select the mode.
(Access point by default) |
| 7 | Radio SSID | AP_37A26230014 | In this text box the user should specify the SSID number which usually comes with the router. |
| 8 | Radio Authentication | WPA2 Personal (PSK) | In this dropdown the user should select the type of authentication.
(WPA2 Personal (PSK) by default) |
| 9 | Radio Encryption | AES | In this dropdown the user should select the type of encryption required.
(AES by default) |
| 10 | Radio Passphrase | ********* | In this text box the user should specify the password. Password will be given with the router which can be changed later. |
| 11 | Radio DHCP server IP | 192.168.100.1 | In this text box the user should specify the IP address of DHCP server.
(192.168.100.1 will be default which can be changed accordingly) |
| 12 | Radio DHCP start address | 100 | In this text box the user should specify the start address of the DHCP.
(100 value is default) |
| 13 | Radio DHCP limit | 50 | In this text box the user should specify the limit for the DHCP.
(50 value is default) |
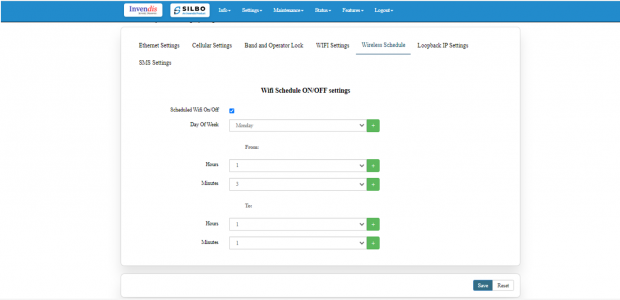
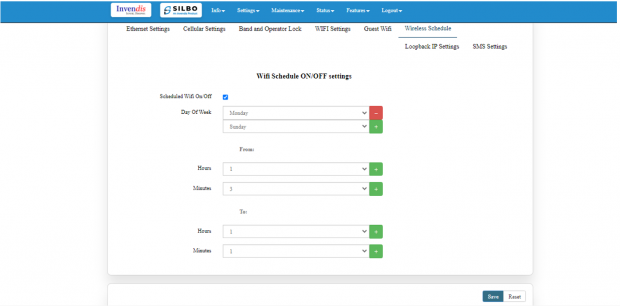
Wireless Schedule:
Wi-Fi can be automatically withdrawn based on the configuration done in this section.
The user can schedule the Wi-Fi’s accessibility time during a particular period.
Note: This section is turned off by default, tick the box to activate it.
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on save and then click on update to update all the required information.
The user can select more than one “day of the week” for scheduling the Wi-Fi working hours.
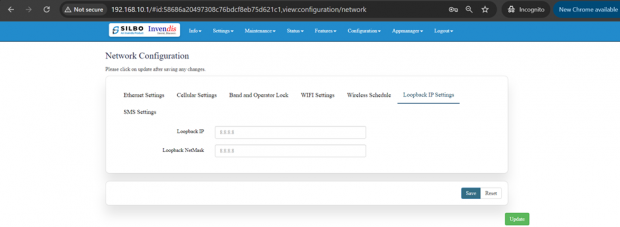
Loop back IP settings:
The loopback IP address, often referred to as “localhost.” it is used to establish network connections within the same device for testing and troubleshooting purpose.
The loopback IP address, commonly represented as 127.0.0.1, is a special address used for testing network connectivity on a local machine.
It allows a device to send network messages to itself without involving external networks, making it useful for troubleshooting and diagnostics.
However, this IP can be changed as per requirement and to do that, Navigating to Setting>>Network configuration>> Loopback IP settings can be changed/updated.
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on the save and then click on the update to update the all the required information.
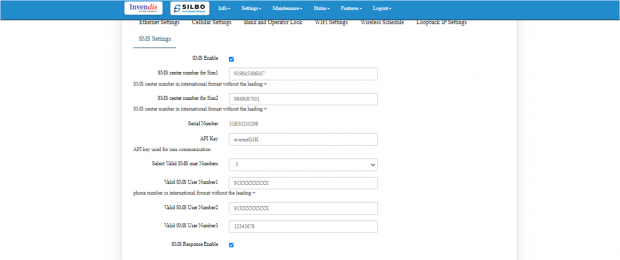
SMS Settings:
User needs to enable SMS option in SMS settings page.
This option is to validate the mobile numbers using which controlling commands could be sent to the router device.
1 to 5 mobile numbers can be authenticated by choosing from “Select Valid SMS user numbers” and adding the mobile numbers below respectively.
API key is the pass key used in the commands while sending SMS.
Displayed in the below screen is the default API key which can be edited and changed as per choice. After addition of the mobile number’s user needs to click on save button for changes to take place.
1.) Select valid user number max. 5 and add authorized phone number in the tab where you want to find the alert and click on ‘SMS Response Enable’, ‘save’ and ‘update’ button.
2.) Now send SMS commands from the configured mobile number.
3.) Once the commands are received from the user phone number the board will send acknowledgement as per the commands.
4.) After that it will send the router’s status once it has rebooted and is operational again.
Mentioned below are a few commands which can be sent from the configured mobile number to the router device. Below two commands are One for rebooting the router device and another to get the uptime.
1) {"device”: ["passkey”, “API key"],"command":"reboot","arguments":"hardware"}
2) {"device”: ["passkey ","API key"],"command”: “uptime"}
After configuring all the required information, the user should click on save and then click on update to update all the required information.
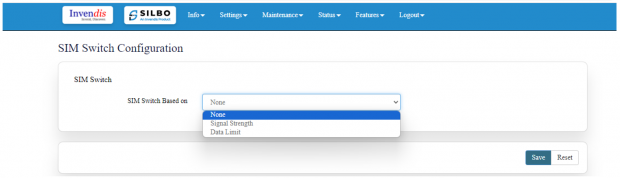
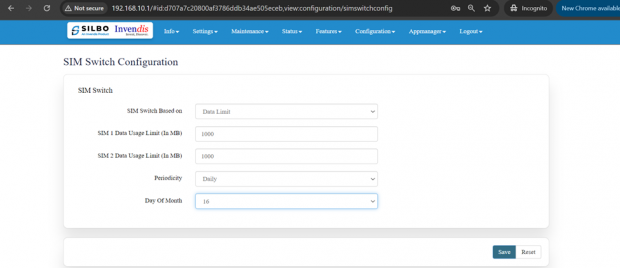
2.2 SIM Switch
In this page the user needs to configure the Sim for the given device.
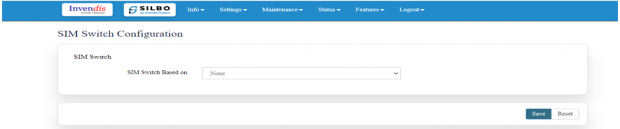 The user needs to select from the drop-down menu on which basis the sim needs to be switched.
The user needs to select from the drop-down menu on which basis the sim needs to be switched.
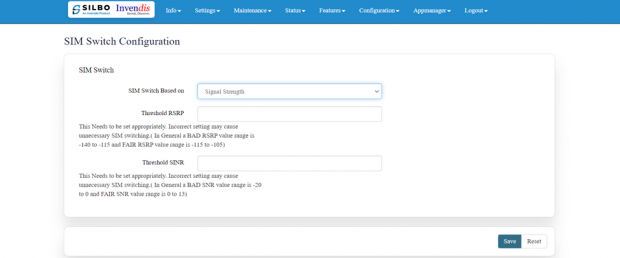
Once the user selects on “signal strength” then the parameters related to signal strength will pop up and the user needs to configure the parameters based on the requirement.
Threshold RSRP:
This Needs to be set appropriately. Incorrect setting may cause unnecessary SIM switching. (In General, a BAD RSRP value range is -140 to -115 and FAIR RSRP value range is -115 to -105).
Threshold SINR:
This Needs to be set appropriately. Incorrect setting may cause unnecessary SIM switching. (In General, a BAD SNR value range is -20 to 0 and FAIR SNR value range is 0 to 13)
Once the user selects on “Data Limit” then the parameters related to Data Limit will pop up and the user needs to configure the parameters based on the requirement.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | SIM Switch Based on | Data Limit | The user needs to select from the drop-down menu on what basis the sim needs to be switched. |
| 2 | SIM 1 Data Usage Limit (In MB) | 1000 | The user needs to set the limit for the data usage for SIM 1. |
| 3 | SIM 2 Data Usage Limit (In MB) | 1000 | The user needs to set the limit for the data usage for SIM 2. |
| 4 | Periodicity | Daily | The user needs to set the pattern/frequency to switch the sims. |
| 5 | Day Of Month | For Ex: 16 | The user needs to set the day for switching the sim. |
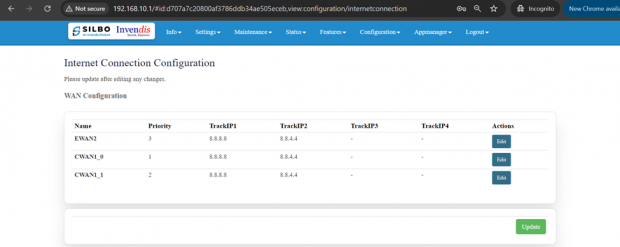
2.3 Internet
In this page the user needs to configure the internet connection to set the priority from the diverse options. The user should decide what kind of connection it needs to provide to the device like LAN, WAN etc. Once the connections are configured then click on save option and then on update.
If the user needs to edit on the existing configuration, then the user should click on the “EDIT” button.
The specifications details are below.
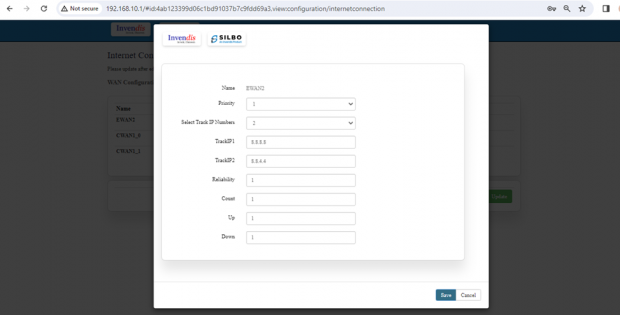
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Name | EWAN2 | This field displays the name of the WAN connection |
| 2 | Priority | 1 | In this dropdown box the user needs to select the priority. |
| 3 | Select Track IP Numbers | 2 | In this dropdown the user needs to select the track number for the Ips. This specifies the number of IP addresses that will be used for tracking the status of the connection. |
| 4 | TrackIP1 | 8.8.8.8 | This is the first IP address used for tracking the connection. 8.8.8.8 is a public DNS server provided by Google.
|
| 5 | TrackIP2 | 8.8.4.4 | This is the second IP address used for tracking the connection. 8.8.4.4 is another public DNS server provided by Google.
|
| 6 | Reliability | 1 | This indicates the reliability threshold for considering the connection as up. A value of 1 typically means that only one successful ping response is needed to deem the connection reliable.
|
| 7 | Count | 1 | This specifies the number of consecutive pings sent to the track IP addresses. |
| 8 | Up | 1 | This indicates the number of successful pings required to consider the connection as up. |
| 9 | Down | 1 | This indicates the number of failed pings required to consider the connection as down. |
Once the user is done with modification click on the save button to save all the changes and then click on the update button.
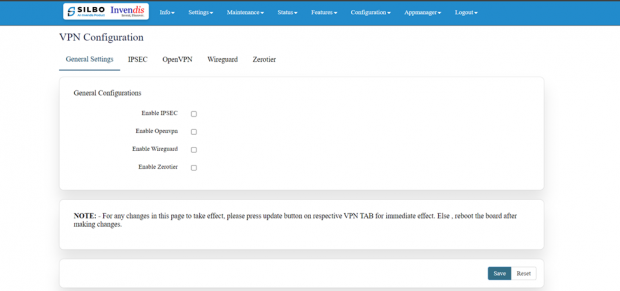
2.4 VPN
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, it establishes a connection between the system and a remote server, which is owned by a VPN provider.
Creating a point-to-point tunnel that encrypts the personal data, masks the IP address, and allows to block the required website to blocks via firewalls on the internet.
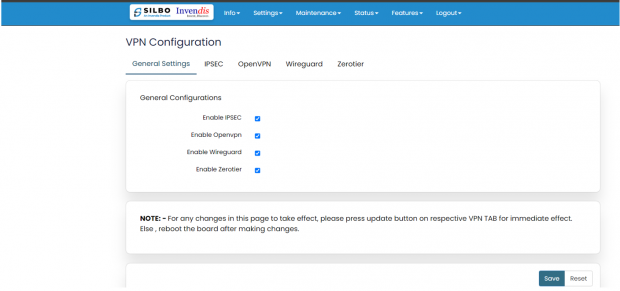
Navigate to settings >= VPN, general settings and you will see all VPN options you wish to use.
Refer the below figure.
There are 5 types of setting available under VPN configuration.
- General Settings
- IPSEC
- Open VPN
- Wireguard
- Zerotier
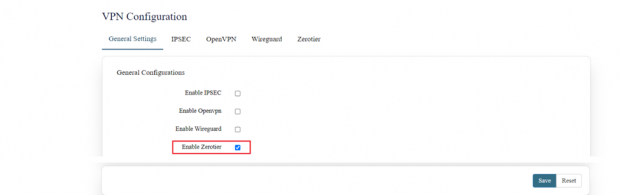
General Settings:
In this page the user must choose which type of VPN connection is required for the device. The user must select from IPSEC, Open VPN, Wireguard or Zerotier based on its requirement. If required, the user can select all the options. The user needs to click on the save after selecting the option based on its use.
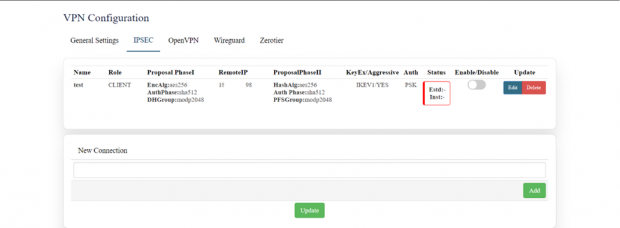
IPSEC:
IPSEC VPN is used to create a VPN connection between local and remote networks.
To use IPSEC VPN, the user should check that both local and remote routers support IPSEC VPN feature.
In this page the user can add/edit/delete the IPSEC VPN connection for the device.
The user needs to click on the update button once the required configuration is completed.
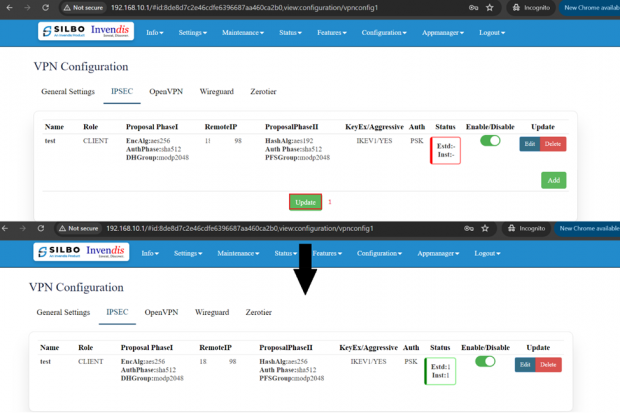
In IPSEC the user needs to click on edit button to edit the configuration of an existing VPN connection.
Click on update once done with configurations.
The tunnel will show established, showing the connection has been made.
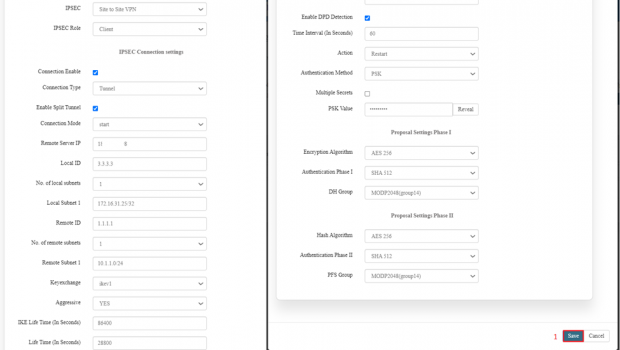
Detailed specifications are below:
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | IPSEC | Site to Site VPN | In this dropdown the user should select the IPSEC connection type. |
| 2 | IPSEC Role | Client/Server | In this dropdown box the user needs to select the IPSEC role. The device is acting as a client in the VPN setup (in this example). |
| 3 | Connection Type | Tunnel | In this dropdown the user needs to select the connection type. The user should select on the connection enable check box. |
| 4 | Connection mode | Route/add/start/trap | In this drop down list the user should select the mode for the connection. In this example start is selected which means the VPN connection is initiated automatically. |
| 5 | Remote Server IP | ******** | The IP address of the remote VPN server. |
| 6 | Local ID | 3.3.3.3 | The user needs to set the local id. It is the identification for the local VPN client. |
| 7 | No. of local subnets | 1 | In this dropdown the user needs to select how many subnets will be connected. |
| 8 | Local Subnet 1 | 172.16.31.25/32 | In this text box the user needs to put the specific local subnet included in the VPN. |
| 9 | Remote id | 1.1.1.1 | In this text box the user needs to put the id of the remote connection. It is the identification for the remote VPN server. |
| 10 | No of remote subnet | 1 | In this dropdown the user needs to select how many subnets it will be connected remotely. |
| 11 | Remote subnet | 10.1.1.0/24 | In this text box the user needs to put the address of the remote subnet. The specific remote subnet included in the VPN. |
| 12 | Key exchange | Ikev1 | In this dropdown the user should select the which key exchange version to be selected. |
| 13 | Aggressive | Yes/No | In this dropdown the user should select either yes or no. |
| 14 | IKE Lifetime (In Seconds) | 86400 | The lifetime of the IKE phase in seconds (1 day). |
| 15 | Lifetime (in seconds) | 28800 | The lifetime of the IPsec SA (Security Association) in seconds (8 hours). |
| 16 | Enable DPD Detection | 1
0 |
Indicates whether Dead Peer Detection is enabled to detect a lost connection. Enable this option as per server-side settings. |
| 17 | Time Interval (In Seconds) | 60 | This option is available only if DPD Detection is enabled. The time interval is the interval for DPD checks. |
| 18 | Action | Restart/clear/hold/
trap/start |
Restart: Action to take when DPD detects a lost connection (restart the connection). Select as per server-side setting. |
| 19 | Authentication Method | PSK | PSK: Pre-shared key is used for authentication. Select this option for authentication as per sever side setting. |
| 20 | Multiple Secrets | 1/0 | Indicates whether multiple PSK secrets are used. Enable only if required. |
| 21 | PSK Value | ****** | Pre-shared key value (masked for security). |
| Proposal settings Phase I | ||||||
| 22 | Encryption Algorithm | AES 128
AES 192 AES 256 3DES |
AES 256: Encryption algorithm for Phase I. Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
| 23 | Authentication Phase I | SHA1
MD5 SHA 256 SHA 384 SHA 512 |
SHA 512: Authentication algorithm for Phase I.
Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
| 24 | DH Group | MODP768(group1)
MODP1024(group2) MODP1536(group5) MODP2048(group14) MODP3072(group15) MODP4096(group16) |
MODP2048 (group14): Diffie-Hellman group for key exchange.
Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
| Proposal settings Phase II | ||||||
| 25 | Hash Algorithm | AES 128
AES 192 AES 256 3DES |
AES 256: Encryption algorithm for Phase II. Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
| 26 | Authentication Phase II | SHA1
MD5 SHA 256 SHA 384 SHA 512 |
SHA 512: Authentication algorithm for Phase II.
Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
| 27 | PFS Group | MODP768(group1)
MODP1024(group2) MODP1536(group5) MODP2048(group14) MODP3072(group15) MODP4096(group16) |
MODP2048 (group14): Perfect Forward Secrecy group.
Select as per server-side configuration. Both server and client should have same configuration. | |||
Click on save and then update the page for changes to reflect.
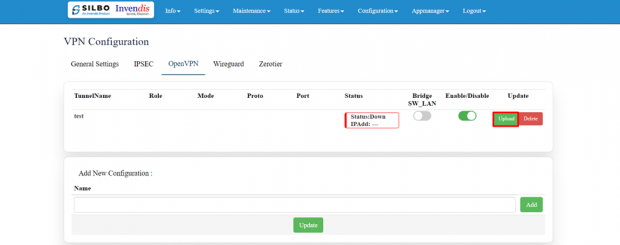
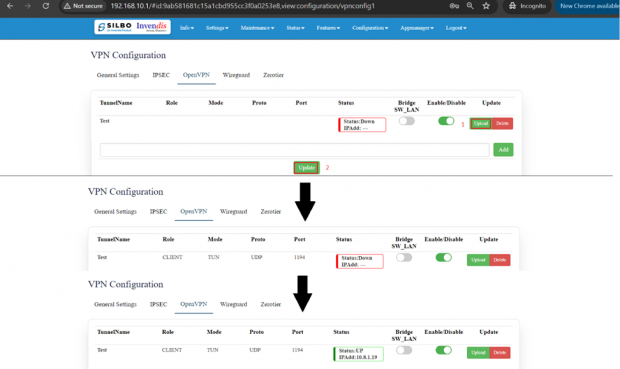
Open VPN:
In the OpenVPN connection, the home network can function as a server, and the remote device can access the server through the router which acts as an OpenVPN Server gateway.
To use the VPN feature, the user should enable OpenVPN Server on the router, and install and run VPN client software on the remote device.
The user needs to “upload” the respective certificate from a valid path and then click on the “Update.”
Once the OpenVPN connection starts the user will get an option to enable/disable the VPN connection as and when required.
By clicking on the enable/disable button, the user can start/stop the VPN connection.
VPN has been established.
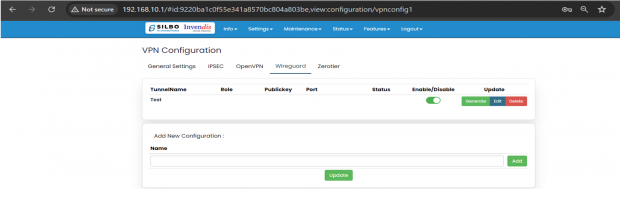
WireGuard:
WireGuard is simple, fast, lean, and modern VPN that utilizes secure and trusted cryptography.
Click on “Edit” to start configurations as needed.
EDIT:
Click on the save button after the required configuration.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
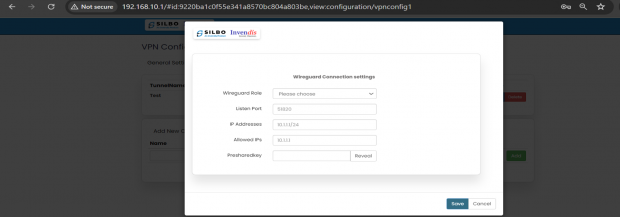
| 1 | Wireguard Role | Client/Server | In this dropdown box the user needs to select the wireguard role. |
| 2 | Listen Port | 51820 | The UDP port on which the WireGuard client listens for incoming connections. |
| 3 | IP Addresses | 10.0.0.1/24 | The IP address and subnet mask assigned to the WireGuard client's interface. This address is used within the VPN. |
| 4 | Allowed PeerIPs | 10.1.1.1 | The IP address of the allowed peer(s) that can connect to this WireGuard client. This might need adjustment based on the actual peer IPs used in the network. |
| 5 | Endpoint HostIP | 10.1.1.1 | The IP address of the WireGuard server (the endpoint to which the client connects). |
| 6 | Endpoint HostPort | 51820 | The port on the WireGuard server to which the client connects. |
| 7 | PeerPublicKey | ***** | The public key of the peer (the server) the client is connecting to. This key is part of the public-private key pair used in WireGuard for encryption and authentication. |
| 8 | Enable Preshared key | Yes/No | This option indicates that a pre-shared key (PSK) is used in addition to the public-private key pair for an extra layer of security. |
| 9 | Preshared key | ***** | The actual pre-shared key value shared between the client and the server. This option appears only if you have enabled preshared key. |
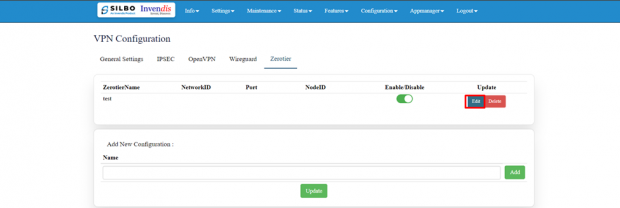
Zerotier:
ZeroTier is a tool that lets you create your own private network over the internet.
Go to ZeroTier Central and sign up for a free account. In ZeroTier Central, click on "Create a Network". This will generate a unique 16-digit network ID for your new network.
Go to settings => VPN, in general settings, enable ZeroTier and save.
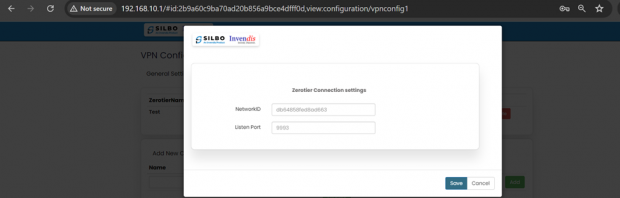
Copy and paste the unique 16-digit network ID in the edit section.
Click on the save button after the required configuration.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | NetworkID | Ad2769hfkw2345f4 | In this dropdown box the user needs to paste the unique 16-digit network id. |
| 2 | Listen Port | 9993 | Default |
2.5 Firewall
A firewall is a layer of security between the network and the Internet. Since a router is the main connection from a network to the Internet, the firewall function is merged into this device. Every network should have a firewall to protect its privacy.
There are 6 types of setting available under firewall.
- General Settings
- Port forwards
- Traffic Rules
- SNAT traffic Rules
- Parental Control
- Zone Forwarding
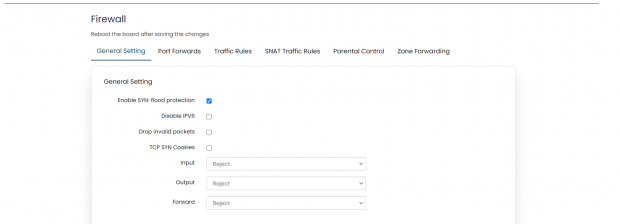
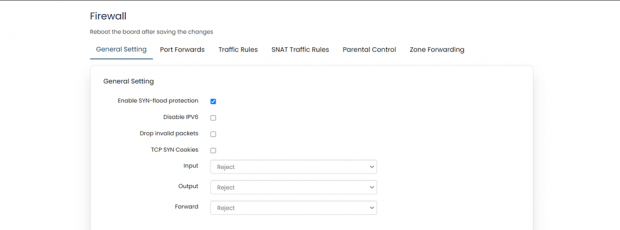
General Settings:
General settings are subdivided into 2 parts,
1.) General settings
In general settings, the settings that are made are default settings and can be changed according to user’s preference.
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Enable SYN-flood protection | Enabled | This is enabled by default; setting can be changed if required. |
| 2 | Disable IPV6 | Disabled | This is enabled by default; setting can be changed if required. |
| 3 | Drop invalid packets | Disabled | This is enabled by default; setting can be changed if required. |
| 4 | TCP SYN Cookies | Disabled | This is enabled by default; setting can be changed if required. |
| 5 | Input | Reject/Accept | By default, the setting is ‘Reject’ but this needs to be changed to ‘Accept’ compulsory. |
| 6 | Output | Reject/Accept | By default, the setting is ‘Reject’ but this needs to be changed to ‘Accept’ compulsory. |
| 7 | Forward | Reject/Accept | By default, the setting is ‘Reject’ but this needs to be changed to ‘Accept’ compulsory. |
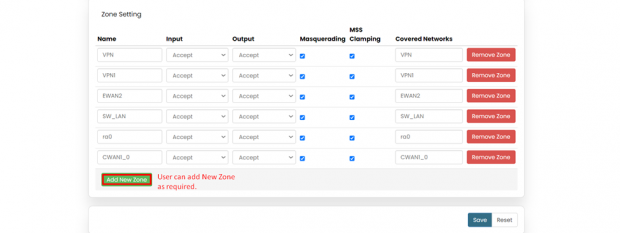
2.) Zone settings
In zone settings, there’s an option to add “New Zone”, according to user’s requirement.
Port Forwards:
Port forwarding is a feature in a router or gateway that allows external devices to access services on a private network.
It maps an external port on the router to an internal IP address and port on the local network, enabling applications such as gaming servers, web servers, or remote desktop connections to be accessed from outside the network.
This helps in directing incoming traffic to the correct device within a local network based on the port number, enhancing connectivity and accessibility.
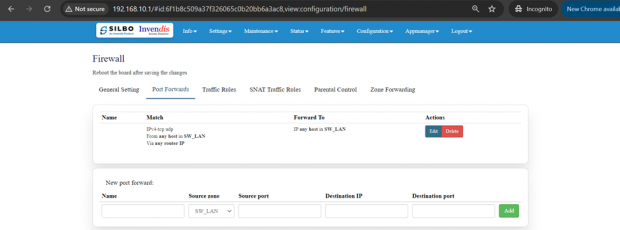 EDIT:
EDIT:
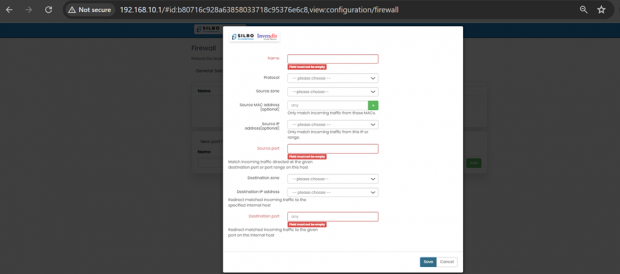
Click on the save button after the required configuration.
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Name | Example: Web_Server_Forward
|
Field must not be empty. Provide a name for the rule to easily identify it. |
| 2 | Protocol | Example: TCP+UDP
|
Select the protocol for the rule.
Options typically include TCP+UDP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, Custom. |
| 3 | Source zone | Example: SW_LAN
|
Select the source zone where the traffic is originating from. Options typically include EWAN2,SW_LAN,CWAN1,CWAN1_0,CWAN1_1,VPN |
| 4 | Source MAC address [optional] | Example: any
|
any: Leave as any if you don't want to specify a MAC address.
|
| 5 | Source IP address[optional] | Example: Leave blank if not needed. | Optionally specify an IP address or range. |
| 6 | Source port | Example: 80, 443 (if matching traffic for web server ports)
|
Specify the source port or port range. |
| 7 | Destination zone | Example: SW_LAN
|
Select the destination zone where the traffic is heading to. |
| 8 | Destination IP address | Leave blank if not needed. | Optionally specify the destination IP address or range. |
| 9 | Destination port | Example: 80 (if redirecting to a web server port)
|
Specify the destination port or port range. |
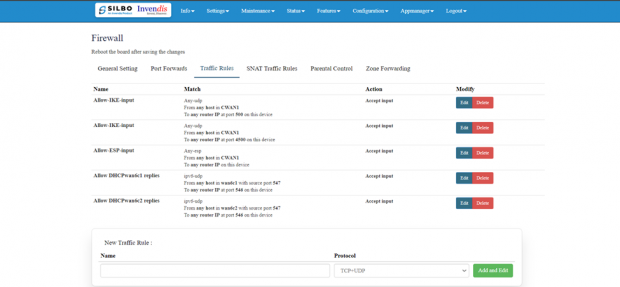
Traffic Rule:
"Traffic rules" refer to the policies and regulations that govern the flow of data packets within a network.
To allow new traffic, click on “Add and Edit” in “New Traffic Rule”.
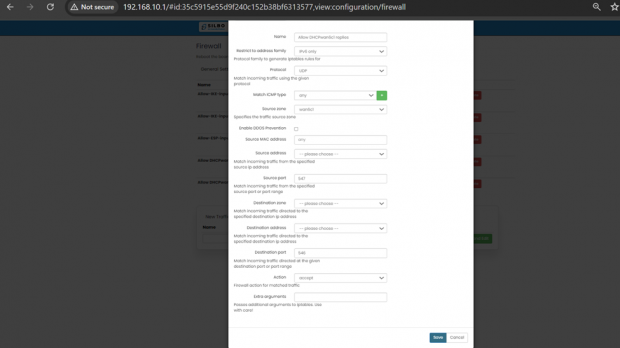
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Name | Example: Allow_HTTP_and_HTTPS | Field must not be empty: Provide a descriptive name for the traffic rule. |
| 2 | Restrict to Address Family | 1. Options: IPv4, IPv6
Example: IPv4 if dealing with typical internet traffic. |
Select the address family to generate iptables rules for. |
| 3 | Protocol | Example: TCP+UDP | TCP+UDP: Match incoming traffic using the given protocol. |
| 4 | Match ICMP Type | Example: any | Match all ICMP types if set to any. Specific types can be chosen if needed. |
| 5 | Source Zone | Example: LAN | Specifies the traffic source zone. |
| 6 | Enable DDoS Prevention | Example: ‘Checked’ if you want to enable DDoS prevention measures | Enable or disable Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) prevention. |
| 7 | Source MAC Address | Example: any | any: Match traffic from any MAC address or specify a particular MAC address. |
| 8 | Source Address | Example: 192.168.1.0/24 | Match incoming traffic from the specified source IP address or range. |
| 9 | Source Port | Example: any if all source ports should be matched | any: Match incoming traffic from the specified source port or port range. |
| 10 | Destination Zone | Example: WAN | Specifies the traffic destination zone. |
| 11 | Action | Example: ACCEPT | Options: ACCEPT, DROP, REJECT. Specify the action to take for matched traffic. |
| 12 | Limit | Example: 10/minute to limit matches to 10 times per minute. | Maximum average matching rate; specified as a number, with an optional /second, /minute, /hour, or /day suffix. |
| 13 | Extra arguments | Example: --log-prefix "Blocked: " to add a log prefix to log messages for this rule. | Passes additional arguments to iptables. Use with care as it can significantly alter rule behaviour. |
Click on save once configured.
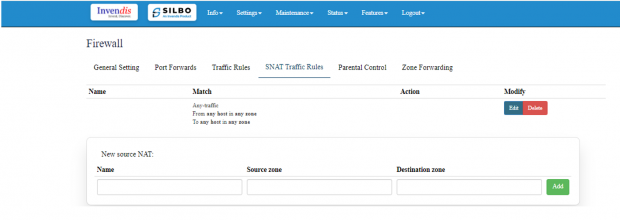
SNAT Traffic Rule:
For configuring SNAT (Source Network Address Translation) traffic rules, you can control how outbound traffic from your local network is translated to a different IP address as it exits the network.
To add new source NAT,
Click on “ADD” in “New Source NAT:”
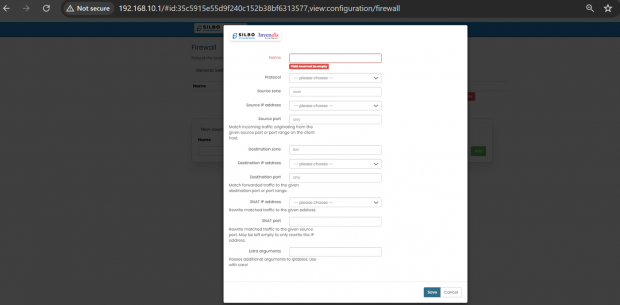
EDIT:
Specification details are below:
| SN | Field name | Sample value | Description |
| 1 | Name | Example: SNAT_WAN_to_LAN | Field must not be empty: Provide a unique and descriptive name for the SNAT rule. |
| 2 | Protocol | Example: TCP+UDP | TCP+UDP: Select the protocols that the SNAT rule will apply to. |
| 3 | Source Zone | Example: wan | wan: Specifies the source zone from which the traffic originates. |
| 4 | Source IP Address | Example: any or a specific range like 192.168.1.0/24 | -- please choose --: Specify the source IP address or range. Leave empty if the rule applies to any source IP. |
| 5 | Source Port | Example: any | any: Specify the source port or port range from which the traffic originates. |
| 6 | Destination Zone | Example: lan | lan: Specifies the destination zone to which the traffic is directed. |
| 7 | Destination IP Address | Example: any or a specific IP like 192.168.1.100 | -- please choose --: Specify the destination IP address or range. Leave empty if the rule applies to any destination IP. |
| 8 | Destination port | Example: any | any: Specify the destination port or port range to which the traffic is directed. |
| 9 | SNAT IP Address | Example: 203.0.113.5 (an external IP address) | -- please choose --: Specify the IP address to which the source IP should be translated. |
| 10 | SNAT Port | Example: Leave empty if not needed, or specify a port like ‘12345’ | Optionally, rewrite matched traffic to a specific source port. Leave empty to only rewrite the IP address. |
| 11 | Extra Arguments | Example: --log-prefix "SNAT_traffic: " (to add a log prefix to log messages for this rule) | Pass additional arguments to iptables. Use with care as it can significantly alter rule behaviour. |
Click on save once configured.
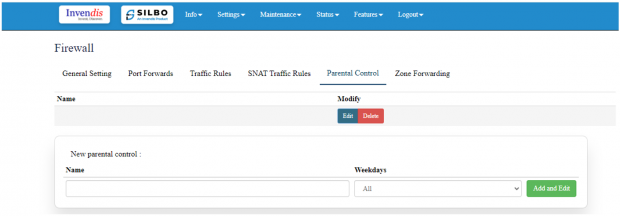
Parental Control:
For configuring parental control rules, you want to set restrictions based on time, source, and
destination zones, as well as specific devices.
To add parental control in firewall,
Click on “Add and Edit” in “New parental control:” field.
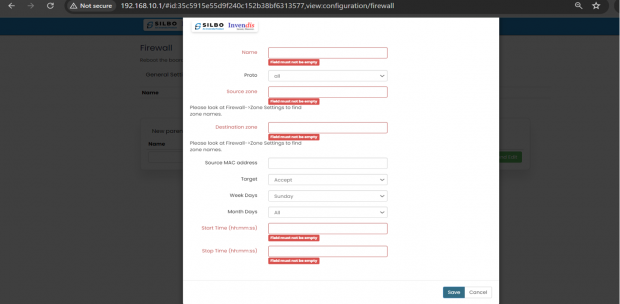
EDIT:
Specification details are given below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Name | Example: Parental_Control_Sunday | Field must not be empty: Provide a unique and descriptive name for the parental control rule. |
| 2 | Proto | all | all: This specifies that the rule will apply to all protocols. |
| 3 | Source Zone | Example: lan | Field must not be empty: Please look at Firewall->Zone Settings to find zone names. |
| 4 | Destination Zone | Example: wan | Field must not be empty: Please look at Firewall->Zone Settings to find zone names. |
| 5 | Source MAC Address | Example: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E | Field: Enter the MAC address of the device you want to apply the parental control rule to. This is useful for restricting specific devices. |
| 6 | Target | Example: Reject | Accept: This specifies the action to take. For parental controls, you might want to use ‘Reject’ or ‘Drop’ to block traffic. |
| 7 | Weekdays | Example: Sunday | Sunday: Specify the days of the week when the rule should be active. |
| 8 | Month Days | Example: All | All: Specify the days of the month when the rule should be active. |
| 9 | Start Time (hh:mm:ss) | Example: 18:00:00 (6:00 PM) | Field must not be empty: Specify the start time when the rule should begin to apply. |
| 10 | Stop Time (hh:mm:ss) | Example: 22:00:00 (10:00 PM) | Field must not be empty: Specify the stop time when the rule should end. |
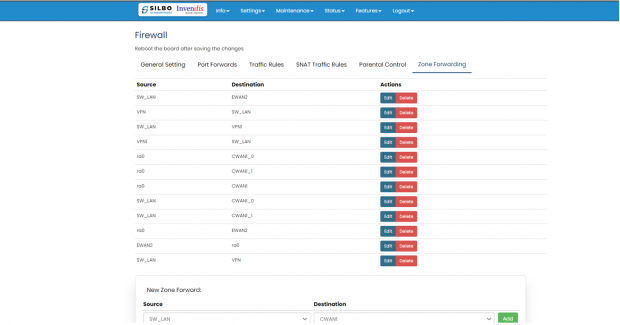
Zone Forwarding:
Zone forwarding in network configuration allows traffic to be directed from one zone to another.
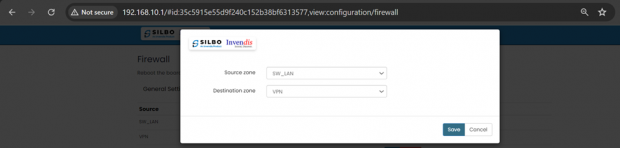
To ADD new zone,
Click on “Add” in “New Zone Forward:” field.
EDIT:
Specification details are below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Source Zone | Example options: lan, wan, etc. | --please choose--: Select the source zone from which the traffic originates. |
| 2 | Destination Zone | Example options: lan, wan, etc. | --please choose--: Select the destination zone to which the traffic is directed. |
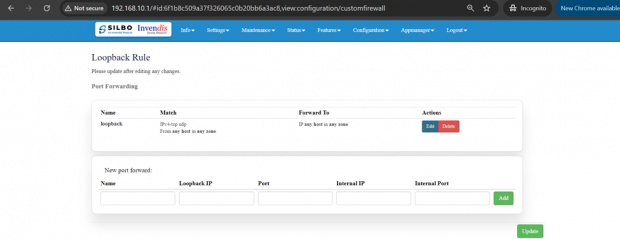
2.6 Loopback Rule
In this page the user can configure the port where he wants to forward the traffic to. Here the user can add/edit/delete different ports as per the requirement.
The user should click on ‘add’ and then ‘edit’ to do the required changes in the port and enter the valid information in each section to configure the port for forwarding.
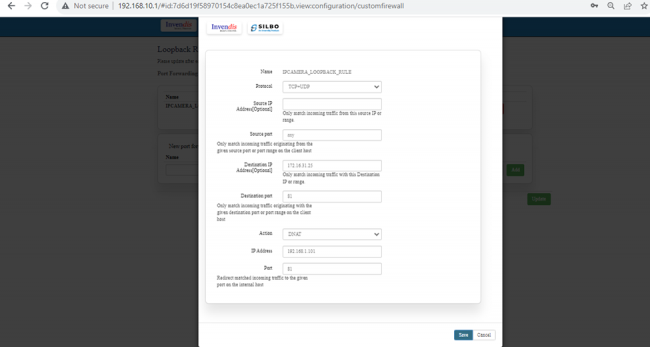
EDIT:
Specification details are given below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Name | Example: loopback | Provide a descriptive name for the rule. |
| 2 | Protocol | Example: TCP+UDP | TCP+UDP: Select the protocols that the rule will apply to. |
| 3 | Source IP Address [Optional] | Example: any or a specific IP range like 192.168.1.0/24 | Optionally specify the source IP address or range. Leave empty if the rule should apply to any source IP. |
| 4 | Source Port [Optional] | Example: any | any: Specify the source port or port range from which the traffic originates. any allows traffic from all ports. |
| 5 | Loopback IP Address | Example: 127.0.0.1 | Specify the loopback IP address. Typically, this is 127.0.0.1. |
| 6 | Port | Example: any | any: Specify the destination port or port range to which the traffic is directed. any allows traffic to all ports. |
| 7 | Action | Example: DNAT | This specifies the action to take either DNAT or SNAT. |
| 8 | Internal IP Address | Example: 192.168.1.100 | Field must not be empty: Specify the internal IP address to which the traffic should be redirected. |
| 9 | Internal Port | Example: any | Redirect matched incoming traffic to the given port on the internal host. |
Once the user is done with the required configurations, should click save button and then click on the update to save the changes.
2.7 Remote Monitoring
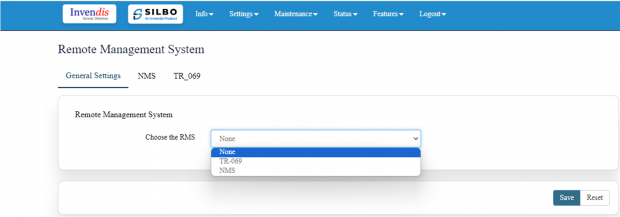
In this page the user can select which equipment needs to be monitored remotely.
Once the user selects the type of RMS click on save.
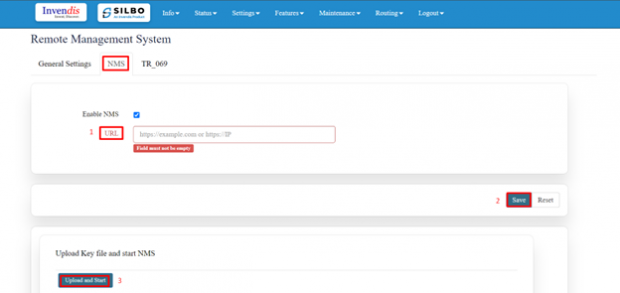
NMS:
IN this page the user should type the server IP or domain name in the URL then click on save.
Click on upload and start (Once key is uploaded and this option is clicked, NMS automatically starts, and this router device gets registered with the NMS server provided).
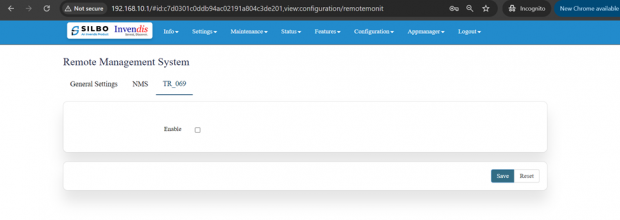
TR_069:
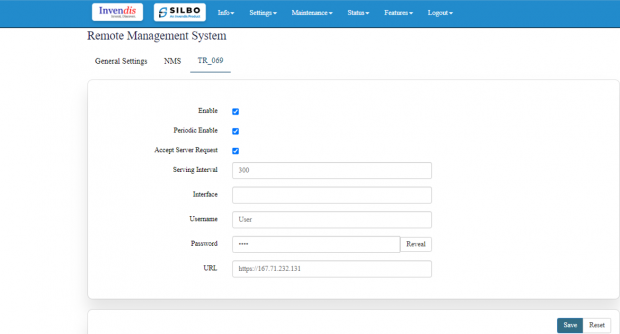
To enable the TR_069 the user needs to click on the enable check box.
Once the user clicks on the check box of enable it will display all the required filed to configured.
Specification details are given below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Serving Interval | 300 | A value of 300 seconds means the device will check in with the ACS (auto-configuration servers) every 5 minutes. |
| 2 | Interface | This can be something like eth0 or wan. | This specifies the network interface used for TR-069 communication. |
| 3 | Username | Example: User | The username used to authenticate with the ACS. |
| 4 | Password | •••• | The password used to authenticate with the ACS. |
| 5 | URL | http://example.com | The URL of the ACS. This is where the CPE (customer-premises equipment) will send its requests and where it will receive configurations and updates from. |
The user should fill all the required fields and click on the save button.
2.8 Tunnel
Tunnels are a method of transporting data across a network using protocols which are not supported by that network.
It is further categorised into 3 sections,
1.) General Settings
2.) GRE Tunnel
3.) IPIP Tunnel
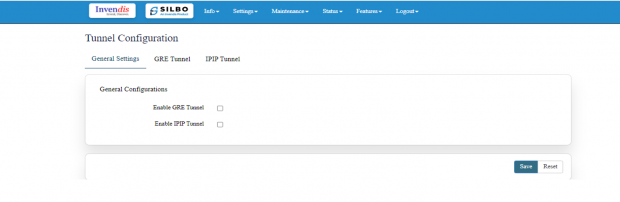
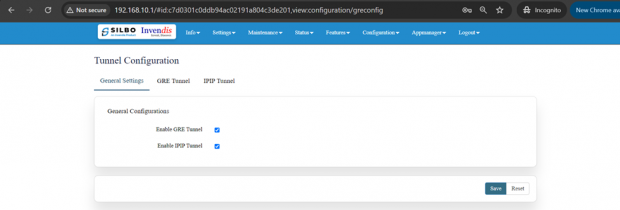
General Settings:
In this page the user needs to select under which type of tunnel it needs to send the data.
Once the user selects the type of tunnel then click on the save button.
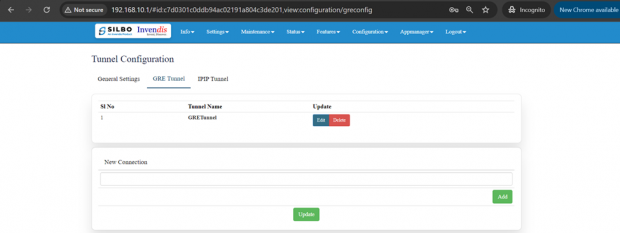
GRE Tunnel:
A GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) tunnel configuration involves setting up a virtual point-to-point connection between two endpoints over an IP network.
Here the user can add/edit/delete the details of the tunnel.
Once the required update is done then click on update to save the changes.
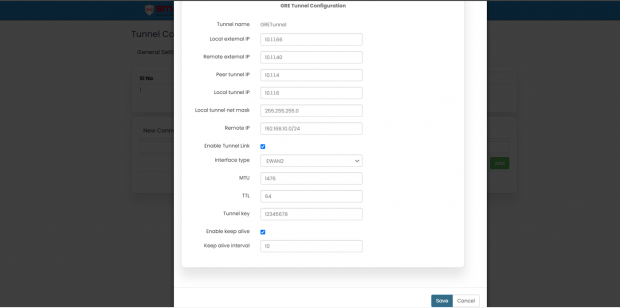
EDIT:
Specification details are given below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Tunnel name | Example: GRETunnel | GRETunnel: The name of the GRE tunnel. |
| 2 | Local external IP | Example: 10.1.1.66 | The IP address of the local endpoint that will initiate the GRE tunnel. |
| 3 | Remote external IP | Example: 10.1.1.40 | The IP address of the remote endpoint that will terminate the GRE tunnel. |
| 4 | Peer tunnel IP | Example: 10.1.1.4 | The IP address of the peer's tunnel interface. |
| 5 | Local tunnel IP | Example: 10.1.1.6 | The IP address of the local tunnel interface. |
| 6 | Local tunnel net mask | Example: 255.255.255.0 | The subnet mask of the local tunnel interface. |
| 7 | Remote IP | Example: 192.168.10.0/24 | The remote network that is reachable through the GRE tunnel. |
| 8 | Enable Tunnel Link | Check to enable | Enable or disable the GRE tunnel link. |
| 9 | Interface type | Example: EWAN2 | EWAN2: The type of network interface used for the GRE tunnel. |
| 10 | MTU | Example: 1476 | 1476: Maximum Transmission Unit size for the GRE tunnel. |
| 11 | TTL | Example: 64 | 64: Time To Live value for the packets within the GRE tunnel. |
| 12 | Tunnel key | Example: 12345678 | 12345678: A unique key used to identify the GRE tunnel. |
| 13 | Enable keep alive | Check to enable | Enable or disable the keep-alive feature to monitor the tunnel's status. |
| 14 | Keep alive interval | Example: 10 | 10: Interval in seconds for the keep-alive packets. |
Once the required update is done then click on update to save the changes.
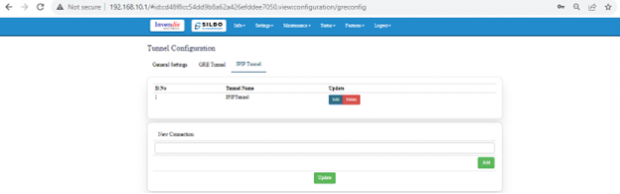
IPIP Tunnel:
An IPIP (IP-in-IP) tunnel is a simple tunnelling protocol used to encapsulate IP packets within IP packets. This is like GRE but without additional features such as keying and type fields.
Here the user can add/edit/delete the details of the tunnel.
EDIT:
Once the required update is done then click on update to save the changes.
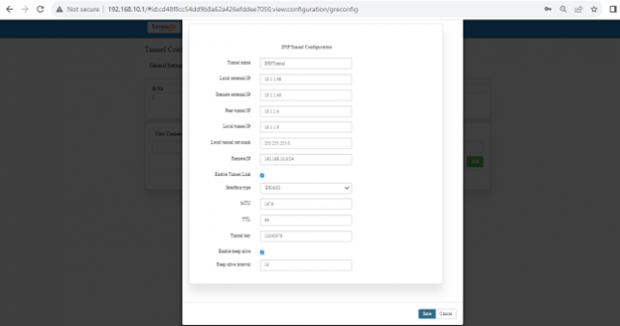
Specification details are given below:
| SN | Field Name | Sample Value | Description |
| 1 | Tunnel name | Example: IPIPTunnel | IPIPTunnel: The name of the IPIP tunnel. |
| 2 | Local external IP | Example: 10.1.1.66 | The IP address of the local endpoint that will initiate the IPIP tunnel. |
| 3 | Remote external IP | Example: 10.1.1.40 | The IP address of the remote endpoint that will terminate the IPIP tunnel. |
| 4 | Peer tunnel IP | Example: 10.1.1.4 | The IP address of the peer's tunnel interface. |
| 5 | Local tunnel IP | Example: 10.1.1.6 | The IP address of the local tunnel interface. |
| 6 | Local tunnel net mask | Example: 255.255.255.0 | The subnet mask of the local tunnel interface. |
| 7 | Remote IP | Example: 192.168.10.0/24 | The remote network that is reachable through the IPIP tunnel. |
| 8 | Enable Tunnel Link | Check to enable | Enable or disable the IPIP tunnel link. |
| 9 | Interface type | Example: EWAN2 | EWAN2: The type of network interface used for the IPIP tunnel. |
| 10 | MTU | Example: 1476 | 1476: Maximum Transmission Unit size for the IPIP tunnel. |
| 11 | TTL | Example: 64 | 64: Time To Live value for the packets within the IPIP tunnel. |
| 12 | Tunnel key | Example: 12345678 | Although typically not used in IPIP, this field might be included for compatibility with certain configurations. |
| 13 | Enable keep alive | Check to enable | Enable or disable the keep-alive feature to monitor the tunnel's status. |
| 14 | Keep alive interval | Example: 10 | 10: Interval in seconds for the keep-alive packets. |